If you could design a diet for men who hate diets—and vegetables—it would be the so-called carnivore diet, in which you subsist on animal foods alone.
Let that sink in for a moment.
You only get to eat animal foods. No fruits. No vegetables. But all the burgers and rib-eye steaks you can get your claws on.
Most people have one of two reactions to this. A) “Are you out of your fucking mind?” Or B) “Sign me up!”
Of all the trends that buck conventional nutrition advice, the carnivore diet may seem like the most radical one yet. It’s one thing to recommend cutting carbs (the ketogenic diet) or eating only plant foods (the vegan diet), but to suggest that animal foods are all you need to be healthy, and that vegetables can actually be detrimental to health is a giant punch in the face to everything we were taught in school and all the recent nutrition and health headlines.
After all, everyone knows that meat is dangerous, especially if you eat a lot of it… right? And that you need at least five servings of fruits and vegetables per day… Or do you?
Well, Onnit investigated the carnivore diet down to the marrow, and found out what happens to your body when you consume animals and nothing else. Here’s our guide to eating meat, bones, and organs for better health. (Spoiler alert: it’s not as crazy as it sounds.)
The Carnivore Diet For Humans
Animals with big teeth and short digestive tracts are meant to eat meat. But what about people? We’re omnivores. Is an all-animal diet even possible for us?
According to Brian St. Pierre, R.D., Director of Performance Nutrition at Precision Nutrition, an education and consulting company (precisionnutrition.com), plant foods aren’t absolutely required in the human diet. “What do we actually need to live? We need protein, fat, and vitamins and minerals in certain amounts,” says St. Pierre. Animal foods—and meat, specifically—can arguably cover those needs (see “Does The Carnivore Diet Create Nutrient Deficiencies?” below). That certainly doesn’t mean that we shouldn’t eat plants, but, from a nutrition standpoint, it isn’t vital that we do, at least for short-term health.
The thing is, though, aside from some isolated tribal people in far corners of the world (such as the Inuits of arctic regions), few people have ever tried to live on animals alone. Those who have did so simply because no other sources of food were available. However, the carnivore diet (also called a zero-carb diet) has recently caught fire. And people are following it by choice!
Why? For many of the same reasons people try a ketogenic diet: weight loss, clearer thinking, fewer digestive problems, and a simple approach to eating that lets them consume foods they enjoy. It may also offer performance benefits. Though scrapping all plant foods seems like a severe step, it instantly removes nearly all of the allergens and antinutrients that some people find cause health problems and discomfort, and, as with ketogenic diets, the lack of carbs alone can offer a range of advantages.
With his appearance on the Joe Rogan Experience podcast in late 2017, and his promotion through the website nequalsmany.com and Instagram (@shawnbaker1967), Shawn Baker is the most famous proponent of the carnivore diet. An orthopedic surgeon and lifelong drug-free athlete, Baker is in his 50s, ripped, and a physical marvel, having recently set two indoor rowing world records. He claims to have eaten only animal products—limiting himself mainly to rib-eye steaks—for more than a year, while suffering no ill health effects and watching his gains in the gym soar.
He hosts an ongoing and informal experiment, encouraging anyone who’s willing to follow the diet to record his/her experience with it, but admits that he hasn’t had his own health officially appraised since he started eating animals only. Rogan, in fact, cringed during their interview when Baker confessed that he hadn’t had any blood work done to check where his cholesterol, triglycerides, and inflammation markers rated. Fortunately, other (human) carnivores have been tested.
But before we discuss the health effects of a carnivorous lifestyle, let’s define exactly what it entails.
Carnivore Diet Food List
The carnivore diet consists of animal foods alone. As long as the constituents of your meal walked, crawled, flew, swam, or otherwise had parents, they’re fair game (no pun intended). You don’t have to follow any rules as far as food timing, macronutrient breakdowns, or portions. Simply eat when you’re hungry and until you’re full. The following are examples of approved carnivore diet foods.
Meat
Steak, burgers, and red meat in general are the main food sources for carnivore dieters. Because you’re not eating carbs—or any plant foods at all—it’s crucial that you get enough calories to keep your energy up, so fattier cuts of meat are best. Poultry and organ meats are also fine, as are processed meat products such as bacon and sausage.
Fish
Any kind is OK, but again, fattier types such as salmon and sardines are the smartest choices.
Whole Eggs
You’ll need the fat in those yolks.
Dairy
Milk, cheese, yogurt, and butter all come from animals and are technically admissible, although most carnivore dieters seem to omit or at least limit them. This is usually due to people discovering the carnivore diet as an outgrowth of the ketogenic diet, in which milk and yogurt are generally not permitted due to their lactose (sugar) content. (See “What’s The Difference Between The Carnivore Diet and The Ketogenic Diet?” below.)
As one of the goals of a carnivore diet is to eliminate nutrients that your body may not be able to process optimally (see “Carnivore Diet Benefits”), you should experiment with dairy foods one at a time and in small doses to see how you handle them. You may find you feel better with none at all.
Bone Marrow
Bone broth is allowed.
Fatty Meat Products
Tallow, lard, and other fat-dense foods derived from meat are greenlit.
Note: Baker doesn’t believe that your food needs to meet USDA organic, pasture-raised or wild-caught standards. However, we do. If you choose to follow the carnivore diet, or consume animal products as a cornerstone of whatever eating philosophy you follow, we strongly suggest that they be of the best quality that you can afford. See our discussion of organic foods in our rebuttal to the documentary What The Health.
Condiments
Salt and pepper are your friends here, as salsa, horseradish, mustard, and various herbs and spices don’t technically qualify. With that said, most sugar-free condiments don’t contain substances that cause digestive problems in most folks, so we don’t see any harm in using them just because they come from plants (especially since people typically enjoy condiments in small servings). With that said, due to its fat content, meat—particularly red meat—is quite flavorful on its own, so you’ll probably find that salt, pepper, or small amounts of butter provide the taste you want without the need for further add-ons.
Supplements
None. Although products such as whey protein and creatine come from animals, there’s virtually no need to supplement with them in this case. Eating animal foods exclusively pretty much guarantees you’ll meet your daily protein needs, and relying on red meat, which is rich in creatine naturally, leaves little reason for further supplementation.
Carnivore dieters who work out do report consuming coffee or caffeine supplements for an energy boost pre-exercise (in spite of the fact that it isn’t an animal product). If you’re concerned that you’re not getting enough micronutrients from your food, a multi-vitamin/mineral supplement may be a good idea.
What’s The Difference Between The Carnivore Diet and The Ketogenic Diet?
The carnivore diet and ketogenic diet both permit protein and fat while restricting carbs, but the carnivore approach is considerably more extreme. Because you aren’t eating any plant foods at all, your carb intake is virtually zero. This isn’t to say that your body won’t have carbs in it though. As with a keto diet, the body learns to make its own carbs to fuel activity in a process called gluconeogenesis. So while the carnivore diet may also be called a “zero-carb” plan, that’s somewhat of a misnomer.
In a ketogenic diet, the emphasis is on fat. Protein is limited in order to prevent excess gluconeogenesis, which can take a person out of ketosis. In the carnivore diet, however, you’re encouraged to eat both protein and fat liberally. As a result, depending on exactly what foods you eat and how much, you may or may not achieve technical ketosis following a carnivore plan. Whether you do or don’t doesn’t matter. The only goal is feeling better and getting healthier.
Unlike with keto, there are no clear guidelines to follow for the carnivore diet regarding macros or percentages of total calories. Because the diet has never been formally studied, there is no hard science to define how to set it up optimally. But Baker and other carnivore dieters seem to agree that relying on red meat makes the diet simple to follow and takes care of every nutritional need.
Remember that your food must be sourced from animals, so the avocados and coconut oil that typically abound on a ketogenic diet have no place in the carnivore plan. On the other hand, you can eat any animal foods you like in any amount or combination you prefer.
Dairy foods containing sugar, such as milk and yogurt, are generally not found in a keto diet plan, but may be included in a carnivore one, even though they contain some carbs.
See the table below for a quick comparison you can use as a reference guide.
| Carnivore Diet | Ketogenic Diet | |
|---|---|---|
| Main Nutrients | Protein and Fat | Fat |
| Amount of carbs allowed | Virtually 0 | 5–20% of calories* |
| Foods allowed | Only animal foods (meat, fish, eggs, bone marrow, some dairy) | Animal and plant foods (coconut oil, avocados, some nuts and seeds) |
*The classic, medically-defined ketogenic diet calls for only five percent of calories to come from carbs, but there are many versions of the diet (including the Mod Keto Diet described HERE) that allow for more and are more appropriate for athletes and active people whose energy needs are greater.
Carnivore Diet Benefits
Eating meat, meat, and more meat may sound like a nightmare to your doctor, but it has some strong advantages backed both anecdotally and by research.
1. Weight Loss
On an all-meat diet? Most people’s first reaction is that you’d get fat, but that’s highly unlikely. As with the ketogenic diet, failing to take in carbs keeps your blood sugar low at all times. You don’t get insulin spikes, so your body has no reason to store incoming calories as body fat. Additionally, the limitations on what you can eat make it almost impossible to get a calorie surplus without a concerted effort.
Ryan Munsey, a performance coach with a degree in food science and human nutrition (ryanmunsey.com), has been on a ketogenic diet for years. Last fall, he experimented with the carnivore diet for 35 days. “I wasn’t trying to lose weight,” he says, “but I went from 188 to 183 pounds in the first week.” Despite the weight loss and the severely restricted food list, Munsey says he never felt the least bit hungry—probably because protein and fat are highly satiating nutrients. To put weight back on, Munsey found that he had to discipline himself to eat two to four pounds of meat daily. “It wasn’t like I was stuffing myself, but it did feel weird at first to eat so much meat.”
If you’re the type who absent-mindedly noshes on nuts, pretzels, or other snack foods, taking in hundreds of calories without even noticing, the carnivore diet can help keep you in check. “You have to be truly hungry to eat,” says Munsey. It may be easy to throw handfuls of popcorn down your gullet, but you can’t accidentally eat a hamburger or cook a steak. You’ll get in the habit of eating only when you need to, and taking in just enough to keep you satisfied. “You learn the difference between physiological hunger and mindless eating,” says Munsey.
Also, though it wasn’t his goal, Munsey’s body stayed in a low level of ketosis throughout the five-week diet (he tested ketone levels to know for sure). “Most people in the keto camp would say if you eat more than a pound of meat a day you’re not going to be in ketosis,” says Munsey. “But I ate up to four pounds a day and I was.”
2. Better Heart Health
First of all, as we explained in our defense of coconut oil last summer, there’s still no clear link between the consumption of saturated fat and heart disease. There is also a solid pile of evidence that saturated fat can potentially improve heart health. Munsey himself found that to be the case.
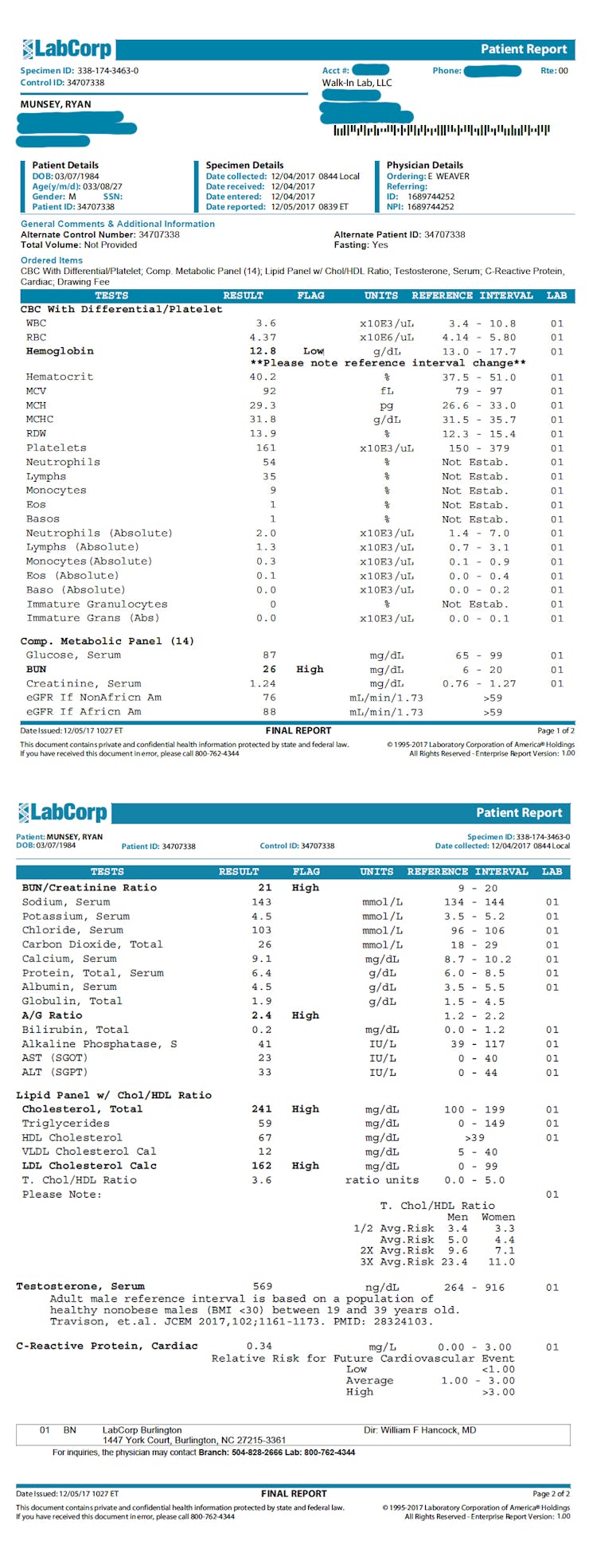
A few months before starting his carnivore diet experiment, Munsey’s blood work revealed that his total cholesterol was 180mg/dL, his HDL level (frequently called the “good” cholesterol) was 57, and his LDL (the so-called “bad” cholesterol) was 123. All good scores. After 35 days of carnivore dieting, he had his numbers checked again.
His total cholesterol climbed to 241mg/dL. While many doctors consider anything over 200 to be too high, part of the reason was the increase in his HDL—it went up 10 points. His LDL went to 162, but his VLDL levels—considered a major marker for heart disease risk—were measured at 12, which is extremely low.
The Mayo Clinic says your cholesterol ratio is a better risk predictor than total cholesterol or LDL. To find it, you divide your total cholesterol number by your HDL score. That gives Munsey a ratio of 3.6 to 1. As 3.4 is considered optimal, he’s in a very healthy range.
Another thing about cholesterol: even though higher LDL numbers are seen as risky, the type of LDL particles you have shuttling through your arteries is most important. If they’re small and dense, they’re considered more dangerous than if they’re bigger and “fluffier.” Therefore, two people with the same LDL value could be at very different levels of risk.
According to the Cooper Institute, a good way to determine what kind of LDL particles you have is to find your ratio of triglycerides to HDL cholesterol. The lower the ratio, the less the risk. Munsey’s triglycerides came in at 59mg/dL, making his triglyceride-to-HDL ratio less than 1, which is exceptional.
Of course, Munsey followed the diet for a very short time, so it’s impossible to predict what would happen to his body long-term, but it should ease your fears about the dangers of meat for the cardiovascular system. Five weeks of eating cow parts didn’t give him a heart attack. In fact, it seemed to reduce his chances of having one. (For more on what he ate specifically, see “Does The Carnivore Diet Create Nutrient Deficiencies?”).
If you don’t believe us, or Munsey, see his official blood lab, direct from his doctor, below.
3. Lower Inflammation
According to some vegans, fat-rich animal foods promote inflammation to a degree that’s on par with smoking cigarettes. The truth, however, is that they can actually lower it. A 2013 study in the journal Metabolism compared subjects who ate a high-fat, low-carb diet to those following a low-fat, high-carb diet. Calories were restricted in both groups, but the high-fat eaters had lower markers of systemic inflammation after 12 weeks. As a result, the researchers concluded that high-fat eating may be more beneficial to cardiovascular health.
The liver produces C-reactive proteins (CRP) in response to inflammation, so measuring CRP levels can indicate how much inflammation is in your system. A level of 10mg/L or less is normal, and 1mg/L or less is good. Munsey’s CRP score post-diet was incredibly low: 0.34.
Simply cutting plant foods from your menu can lower inflammation by itself. “If you had a food sensitivity to some of the plants you were eating and had low-grade inflammation,” says Brian St. Pierre of Precision Nutrition, “then removing them will make you feel better.”
Lower inflammation can mean less achy joints. Plus: “There’s some evidence that eating more gelatinous proteins, as you find in bone broth, collagen, and gelatin,” says St. Pierre, “can improve cartilage health.” This is discussed further in our guide to bone broth.
4. Higher Testosterone
Diets high in fat have been shown to boost testosterone levels. In fact, a study in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that men who followed a high-fat, low-fiber diet for 10 weeks had 13% higher total testosterone than subjects who ate low fat and high fiber. It’s no surprise then that Munsey’s total testosterone levels leaped from 495 ng/dL to 569. Not bad for age 33. “I was pitching a tent first thing every morning,” he says.
5. Fewer Digestive Problems
We’ve been told how important it is to eat fiber our whole lives, and have been sold everything from bran muffins to Metamucil to make sure we get enough. But carnivore dieters think it’s more trouble than it’s worth, and science may prove them right.
A 2012 study in the World Journal of Gastroenterology investigated the effects of reducing fiber intake in people with chronic constipation—the complete opposite of what most doctors would recommend. Subjects were told to consume no fiber whatsoever for two weeks. Then they were allowed to increase their fiber intake to a level they were comfortable with, or follow a high-fiber diet. Incredibly, most of the subjects were doing so well that they opted to continue on the zero-fiber plan. The study lasted six months.
Those who ate high fiber reported no change in their condition, but those who ate no or small amounts of fiber noted significant improvements in their symptoms—including reduced gas, bloating, and straining. Furthermore, the ones on zero fiber actually increased the frequency of their bowel movements!
The reason fiber-filled eating could be problematic for the gut isn’t clear, but carnivore dieters blame certain compounds in plant foods as the source of digestive issues. They cite the book The Plant Paradox, by Steven R. Gundry, M.D., which argues that the natural defense mechanisms that plants contain to dissuade predators cause bloating, gas, and other digestive distress that may make them not worth eating for humans. Lectins, gluten, and phytic acid—common in fruits, greens, beans, grains, nuts, and seeds—can contribute to inflammation and auto-immune disorders such as IBS, Leaky Gut, and more. While this is a controversial opinion (see “Reasons The Carnivore Diet Might Still Be Totally F@#$ing Crazy”), it does provide an explanation for why carnivore dieters claim to feel better than they did eating plants.
“We’ve been told for so long that you need all this fiber,” says Munsey. “But maybe you don’t. Maybe you don’t need any. The carnivore diet challenges what we think we know.”
6. Increased Mental Clarity
Just as with the ketogenic diet, carnivore dieters report thinking more clearly and having better focus almost right away. Again, as with going keto, there is a break-in period where your body has to figure out how to fuel your system without carbs, so you’ll probably feel lethargic and moody at first. You may have difficulty sleeping and even develop bad breath (an early sign that your body is making ketones), but you can ride it out. Within a few days, or just over a week, you could feel sharper than ever. Perhaps even better than if you were doing a standard ketogenic diet (see “The Carnivore Diet for Athletes”). “By the second week, your system comes online,” says Munsey.
7. Simpler Dieting
There’s one thing about the carnivore diet that no one can argue: it’s not complicated. You eat animal foods when you’re hungry, and that’s it. If you’re the type of person who gets confused counting calories or macros, is tired of weighing portions on a food scale, or isn’t sure what’s gluten-free and what isn’t, a carnivore diet will all but relieve you of having to think.
“I started by trying to eat one rib-eye in the morning and one in the afternoon, or the equivalent amount of protein and fat,” says Munsey. “It worked out to be about a pound of meat in the morning and then two in the afternoon. I never measured anything or tracked ratios.” It’s also worth noting that Munsey prefers to follow an intermittent fasting style of eating, having his first meal between 10 a.m. and 12 p.m. and his second between 3 and 5 p.m. But you don’t have to.
“As far as your lifestyle goes, it’s quite enjoyable,” says Munsey. “You get to eat steak and bacon all day. I never got tired of eating meat. I actually started craving it.”
And while a meat-rich diet may sound like it would break the bank, the amounts you actually consume may not be high, since meat is so satiating. That should keep costs down—especially if you literally aren’t buying any other food.
Is The Carnivore Diet Safe?
Because it’s similar to a ketogenic diet, and we’ve already shown that meat isn’t to blame for heart disease, it appears fair to consider the carnivore diet safe for most people—at least in the short term. However, if you’ve ever seen the movie Beverly Hills Cop, there’s one question you’ve been dying to ask: is all that meat going to get stuck in my gut?
In the film, one character reads a (fictitious) article to another, citing science that claims that “by the time the average American is 50, he’s got five pounds of undigested red meat in his bowels.” Based on this one scene in a popular movie from more than 30 years ago—and an Eddie Murphy comedy at that—the urban legend has perpetuated that beef somehow blocks up your intestines, colon… you name it.
However, just as you can’t disable a police car by shoving a banana in its tailpipe (another bit of wacky science from the movie), your body won’t choke itself to death from eating rib-eyes.
“Like most foods, meat is absorbed in the small intestines before it reaches the colon,” says St. Pierre. “The idea that meat gets impacted in your GI tract is silly.” It’s possible to get a bowel obstruction due to disease or physical injury, “but red meat isn’t something that blocks your GI tract.” Since there isn’t much coming out, people who have small bowel movements tend to assume that waste is getting stuck inside them. But St. Pierre says that small movements, including those of carnivore dieters, are simply due to low intakes of fiber. “Fiber adds bulk,” he says. So the reason your poop is small is because it doesn’t have veggies in it.
“I never had any distension, bloating, or water retention throughout the whole process,” says Munsey. “In fact, I felt light and had a bounce in my step.”
A more serious concern on the carnivore diet, however, is the risk of cancer. “There’s so much evidence on phytonutrients from plant foods and how they help with DNA protection,” says St. Pierre. “If you’re not consuming those things, your guess is as good as mine as to how that’s going to impact you long-term.” Bacteria in the GI tract and colon ferment fiber into butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid. Butyrate decreases inflammation in the GI tract, potentially decreasing the risk of colon cancer.
“I would highly suspect that an all-animal diet would increase your risk of colon cancer,” says St. Pierre. Not because animal foods are carcinogenic in any way, but because “you wouldn’t be consuming things that help to inhibit colon cancer. So the dose makes the poison. Having a few servings of red meat each week is no big deal, but when you’re eating three steaks a day with nothing else, that’s a different story. You’re changing the equation substantially.”
Not to mention, eating fruits and vegetables offer benefits for eye health, brain health, and overall longevity, says St. Pierre. “You’d be ignoring so much research on their potential benefits by cutting them all out.”
Another popular carnivore diet question: what happens to the gut biome? That is, the balance of bacteria that help digest your food and prevent disease. Surely, those critters must require some carbs. Or not.
“I had zero dysbiotic flora [the bad bacteria] at the end of the diet,” says Munsey, who had his poo tested. “And I had pretty good numbers on all the beneficial flora.” He chalks it up to the carnivore diet being, if nothing else, an extreme elimination diet that starves sugar-hungry bad bacteria to death. “Yeah, it would starve some of the good ones as well, but maybe we don’t need as many of those. Maybe we only need them if we’re eating a high-plant diet. It’s never been studied, so for people to jump right out and say the carnivore diet is wrong and bad for your health… well, we don’t know that.”
Does The Carnivore Diet Create Nutrient Deficiencies?
The risk of life-threatening illness aside, the carnivore diet—somewhat surprisingly—doesn’t seem to lead to many, if any, serious vitamin or mineral deficiencies. Red meat alone contains copious amounts of iron and zinc, and seafood and dairy supply vitamin D, which usually has to be added to plant foods. The one micronutrient that nutritionists like St. Pierre aren’t sure you’d get enough of is vitamin C, which is otherwise extremely easy to obtain when eating fruits and vegetables.
In rebuttal, carnivore supporters make the argument that, in the absence of carbs, your body may not need much vitamin C, thereby making small intakes sufficient. Stephen D. Phinney, M.D., Ph.D., author of The Art and Science of Low-Carbohydrate Living, has speculated that the ketone beta-hydroxybutyrate—which your body will produce when you remove carbs from your diet—replaces the need for vitamin C, at least in part. On a balanced diet, one of vitamin C’s roles in the body is to form collagen, but Phinney says that the amino acids you get from a large meat intake get the job done without it. Indeed, neither Munsey or Baker have come down with scurvy, and neither have hundreds (thousands?) of other zero-carb dieters at home and abroad—as far as we know.
St. Pierre adds that if you make the effort to eat a diverse range of animal foods—i.e. NOT just rib-eye steaks—you hedge your bets that you’ll get the micronutrition you need. That means venturing beyond lean muscle meats and taking advantage of foods like bone broth and organ meats. That’s what Munsey did. “I was just being extra cautious,” he says. And “organ meats,” he points out, “have more micronutrients than vegetables.”
The Carnivore Diet for Athletes
The ketogenic diet has taken a lot of heat from critics who say that people who exercise must eat carbs to supply fuel, but science has shown that not only is it possible to work out on a low-carb diet, you can even perform at an elite level. But take away ALL carbs and all plant foods and it could be a very different story. The short answer is that we don’t know exactly how a long-term carnivore diet would affect muscle mass, endurance, or overall performance yet. But many carnivore dieters report making some of the best gains of their lives on the plan.
As mentioned above, Shawn Baker is a world-class indoor rowing competitor and deadlifts 700-plus pounds at over 50 years old. He could well be a genetic outlier, but what about Ryan Munsey? Without adding body weight, Munsey made dramatic strength gains on the diet. Below are the improvements he made on his two-rep max in the various lifts he tested. All were accomplished within five weeks of carnivore eating.
Front squat: from 235 pounds to 265
Deadlift: from 335 to 375
Incline bench press: 205 to 220
Weighted pullup: 60 pounds of added weight to 100 pounds
The first week on the diet, Munsey says he felt sluggish and had little motivation to train. But by the second week, he says, he was a “samurai” in the gym. He credits the gains to the increased amount of protein he was eating, as he had been doing a ketogenic diet prior. “With keto, I felt great mentally, but I never felt like doing much physically. On the carnivore diet, I just felt like a warrior.” He was getting 120 to 150 grams of protein per day before when he weighed between 185 and 188 pounds. After adopting a two-to-four-pounds per day meat habit, Munsey estimates his protein intake was between 200 and 300 grams.
It’s worth noting that Munsey did not do cardio, apart from daily walks (he averaged 5,000 steps a day, total). Therefore, it’s difficult to say how he would have fared had he been running, rowing, or doing more metabolically-demanding workouts such as CrossFit. “I think the adaptation period before you would excel again at those activities would be more brutal than what I went through,” says Munsey.
To be fair, Baker claims he needed six months to fully adapt to the diet and get his performance back on track.
“Just because we can live on a carnivore diet,” says St. Pierre, “doesn’t mean we’d necessarily thrive on it. If you’re an intermittent sport athlete, competing in sprinting or something else that requires high output for 60–120 seconds, it would be very challenging to perform well when you’re not eating any carbs. There are people who adapt really well to fat and their performance does improve, but I think performance would suffer for most.” As with any diet, you’ll have to try it and see what happens.
If you are an athlete or gym rat, you may do better to modify the carnivore diet just as we discussed modifying the ketogenic diet HERE. St. Pierre suggests starting by adding some vegetables. “Cruciferous ones like broccoli, cauliflower, and kale would be my vote.” If you find that your workouts are suffering, “maybe that means having the occasional sweet potato or apple,” says St. Pierre.
Carnivore Diet Meal Plan
Here’s an example of how you could eat in a day if you want to get the broadest possible nutrition from an all-animal diet.
Breakfast
Coffee (black, or with whole milk)
Scrambled eggs and bacon
(You may also choose to skip breakfast and fast till lunch)
Lunch
Rib-eye steak, OR chicken liver, seasoned with salt and pepper
Snack
1 cup bone broth, OR a few slices cheese
Dinner
Hamburger patty seasoned with cayenne, onion powder, garlic powder, salt and pepper
OR salmon fillet
All meats and dairy products should be organic and pasture-raised whenever possible
Reasons The Carnivore Diet Might Still Be Totally F@#$ing Crazy
If you’ve made it this far into the article, you’re probably realizing that the carnivore diet isn’t as ridiculous as it may at first sound. Nevertheless, there are some compelling reasons to not try it—or at least not follow it for very long—apart from what we’ve already mentioned.
Environmental Impact
It’s safe to say that, if everyone adopted this diet, the world would run out of animals pretty fast. Supporting organic farming practices and eating locally is a noble, smart way to improve the welfare of animals and reduce pollutants, but drastically increasing the demand for meat would undoubtedly have a detrimental effect on the planet—at least while conventional farming methods remain pervasive.
Vegetables Are Still Good
Carnivore dieters blame digestive problems on plants. Grains, legumes, and nuts are indeed sources of phytic acid, an antinutrient that can prevent the body’s absorption of iron and zinc. But according to St. Pierre, the negative impact it has on your nutrition is minimal. “The data on phytic acid, lectins, and tryptin inhibitors is nowhere near as bad as people like to make it out to be,” says St. Pierre. Plants have innate defense systems to discourage predators from eating them, but that doesn’t mean they can’t or shouldn’t be eaten. Similarly, “a lobster has a shell and claws to defend itself, but that doesn’t mean you can’t eat it,” says St. Pierre.
Also, the way we prepare food reduces the potency of the antinutrients within it. When bread is baked with yeast, the phytic acid content in the grains dissipates. Levels are also low in sprouted-grain and sourdough bread. “At the same time,” says St. Pierre, “in reasonable amounts, phytic acid also has some potential health benefits, one of them being anti-cancer, and it can chelate heavy metals.” One such heavy metal, iron, can be toxic in high amounts. And you risk getting such amounts on an all-meat diet.
This isn’t to say that some people aren’t especially sensitive to certain plant foods. If you know one that bothers you, don’t eat it. But it’s probably best not to weed out every bit of vegetation in your diet based on a reaction to one or two types.
Sustainability
The planet isn’t the only thing that could suffer if you go all meat, all the time. You may end up hating life, no matter how cool the idea of eating burgers and bacon all day sounds to you now. A strict animal diet means no beer, no avocados for your Fajita Night… and, in fact, no fajitas at all (tortillas are a no-no). You can bend the rules and have your cheat days, but then you’re not really doing the diet, are you?
Munsey says he didn’t get many cravings on the carnivore diet, but has since added back some plants and the occasional carbs for the sake of long-term health. “I still pretty much follow the carnivore diet because I love the way I feel on it. But it’s really difficult to do when you travel.” If you can’t find high-quality meat on the road, you need to be careful where you eat out. But that can be part of the thrill of going carnivore, too.
“It’s fun to order two rib-eyes and nothing else and see how the waiter reacts,” says Munsey. “I was in an airport and got four hamburger patties and the manager came out to confirm that my order was right. It definitely throws people off.”






)







